Search Results for: water table
Water table
water table (Science: ecology) The zone of saturation at the highest average depth during the wettest season, it is at least... Read More
Running Water Freshwater Communities
Running water freshwater communities are also known as lotic communities, lotic meaning running water. Lotic communities are... Read More
The Water Cycle
The water cycle (sometimes referred to as the hydrological cycle) is the continuous transfer of water from air, sea land and... Read More
Hypertonic solution
Hypertonic Solution Definition Hypertonic solution is a relative term that describes the solution having a higher amount of... Read More
Hydrophilic
Hydrophilic Definition What does a hydrophile (or hydrophilic molecule) mean? If a molecule is “water-loving”, it is... Read More
Dehydration reaction
What is dehydration synthesis? A dehydration reaction is a form of biochemical reaction wherein a water molecule is lost or... Read More
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of protoplasm away from the cell wall of a plant or bacterium. The protoplasmic shrinking is... Read More
Vascular plants
Definition of Vascular plants The term 'vascular' is derived from the Latin word vāsculum, vās, meaning "a container and... Read More
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a physio-chemical process carried out by photo-auto-lithotrophs by converting light energy into chemical... Read More
Body fluid
Body Fluids Definition What is body fluid? Literally, body fluid is the fluid of the body. The adult human body is ~50-60%... Read More
Abiotic factor
An abiotic factor is a non-living element of the environment that influences the way organisms and ecosystems function. Some... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Hyperosmotic
Hyperosmotic Definition What is hyperosmotic? The word hyperosmotic is derived from two Greek words: 'hyper', meaning... Read More
Alimentary canal
Definition of Alimentary canal What is the alimentary canal? The alimentary canal is a muscular hollow continuous tubular... Read More
Carbon fixation
Carbon Fixation Definition We know that the earth contains many elements. The periodic table shows us just how many... Read More
Disaccharide
Carbohydrates are organic compounds comprised of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, usually in the ratio of 1:2:1. They are one... Read More
Glycolysis
What is Glycolysis and Why is it Important? Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway by which the 6-carbon molecule of glucose is... Read More
Decomposer
Decomposer Definition The organisms that carry out the process of decay or breakdown of the dead organism are known as... Read More
Angiosperm
Angiosperms Definition What is an angiosperm? An angiosperm is a plant that produces flowers. The angiosperms, also... Read More
Metabolism
Metabolism Definition What is metabolism in the body? Metabolism encompasses the various biochemical processes, reactions,... Read More
Residual volume
Residual volume is a term that is most often seen in lung physiology where it is defined as the amount of air remaining in... Read More
Null hypothesis
Null Hypothesis Definition Null hypothesis is defined as “the commonly accepted fact (such as the sky is blue) and... Read More
Density dependent limiting factor
What Is A Density-Dependent Limiting Factor? Density-dependent limiting factors are limiting factors, which, depending on... Read More
Chlorophyll
Why are most plants green? Have you ever had the same question? Perhaps, you’ve been told that the plants are green... Read More
Primary productivity
Planet Earth is home to different types of life forms ranging from microscopic bacteria to giant whales and elephants. To... Read More
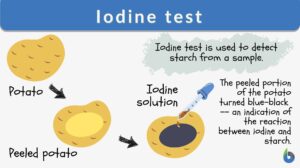
Iodine test
Iodine Test Definition The iodine test is a chemical reaction-based identification test for starch. In this test, iodine... Read More
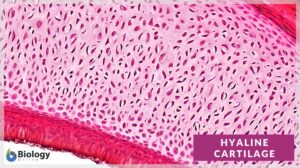
Hyaline cartilage
Hyaline Cartilage Definition Before we define hyaline cartilage, let us understand what cartilage is. What is cartilage? Is... Read More
Aqueous solution
Definition noun, plural: aqueous solutions A solution wherein water is the dissolving medium or solvent Supplement Solution,... Read More